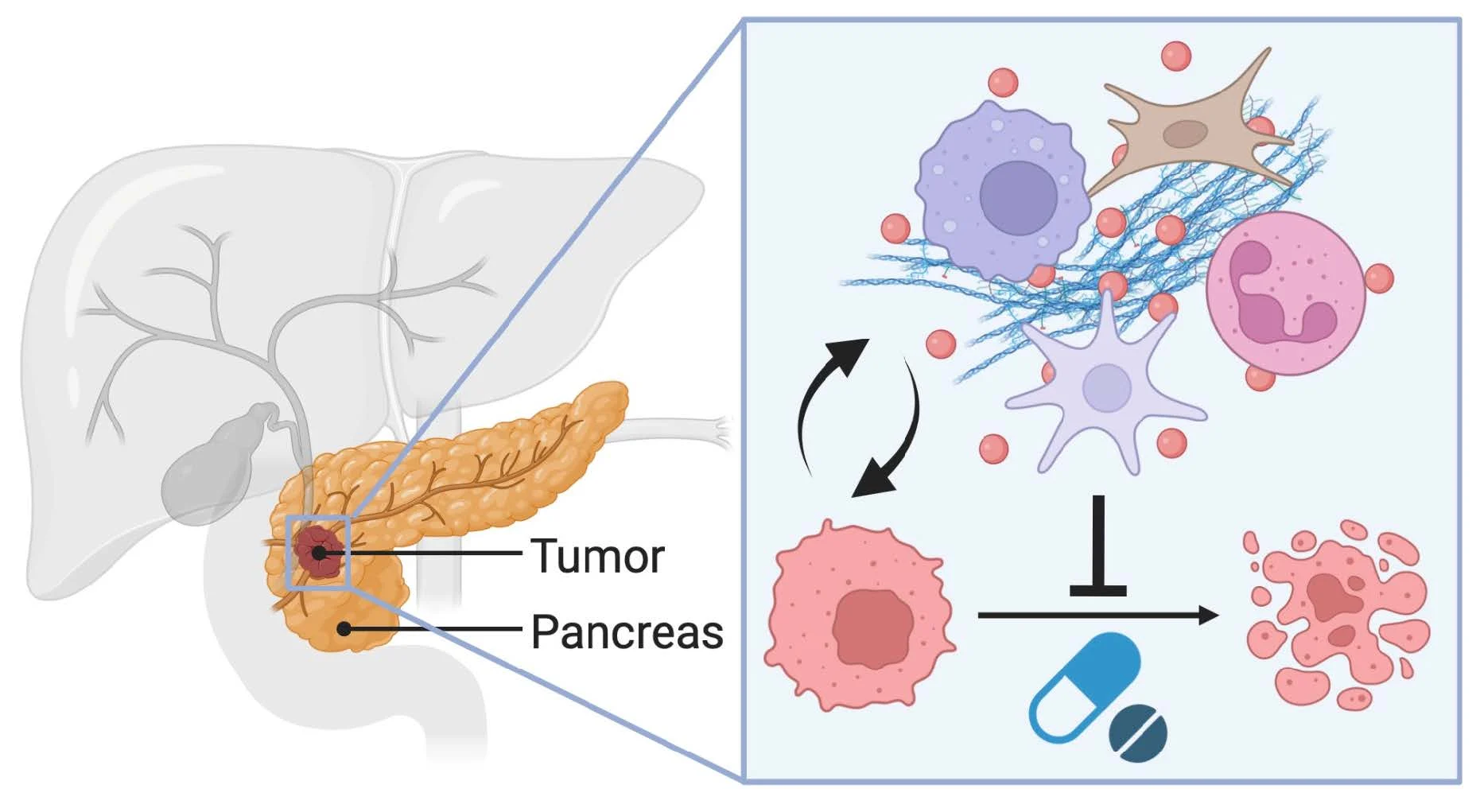
About Pancreatic Tumors
Pancreatic tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the pancreas, an organ located deep in the abdomen that plays a crucial role in digestion and blood sugar regulation. These tumors may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and can affect the pancreas’s ability to function properly.
In many cases, pancreatic tumors grow silently in the early stages, causing few or no symptoms. As the tumor increases in size, it may block bile ducts, interfere with digestion, or spread to nearby organs. Early detection and specialised medical care are essential for effective treatment and improved survival rates.