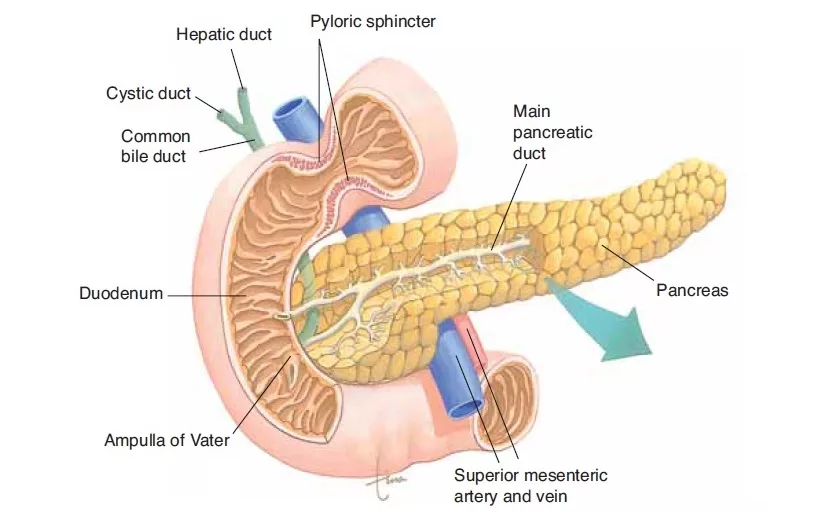
About Pancreatic Pseudocyst
A pancreatic pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops in or around the pancreas, usually as a complication of acute or chronic pancreatitis. Unlike true cysts, pancreatic pseudocysts do not have an epithelial lining; instead, they are surrounded by fibrous or inflammatory tissue. These pseudocysts contain pancreatic enzymes, fluid, and sometimes debris.
Pancreatic pseudocysts commonly form after an episode of pancreatic inflammation or injury. While some pseudocysts may resolve on their own, larger or symptomatic pseudocysts often require medical or endoscopic treatment. Early diagnosis and proper management help prevent serious complications such as infection, rupture, or bleeding.