Liver Tumors Treatment
Liver tumors are abnormal growths that develop in the liver. These tumors may be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and can affect normal liver function if not diagnosed and treated in time. Early detection plays a crucial role in successful treatment and long-term outcomes.
With proper evaluation, advanced diagnostic tools, and a personalized treatment plan, liver tumors can be effectively managed. Timely medical care helps preserve liver function and reduces the risk of complications.
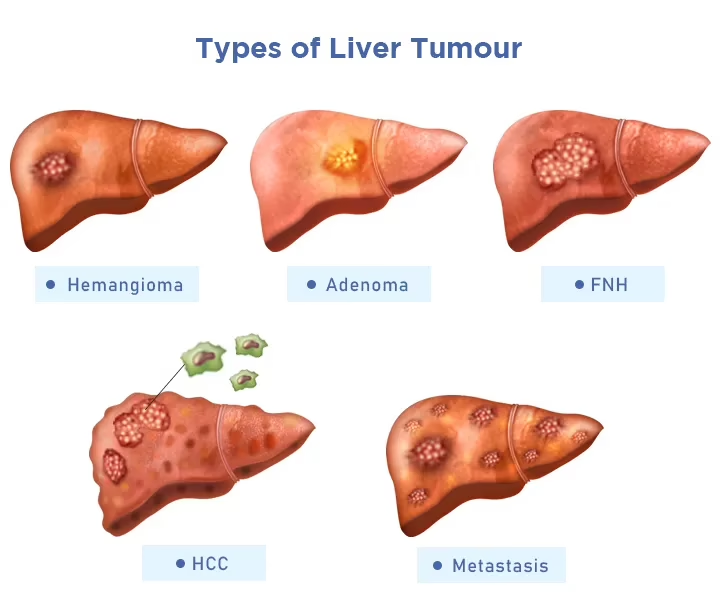
What Are Liver Tumors?
Liver tumors occur when liver cells grow abnormally and form a mass. Some liver tumors are harmless and grow slowly, while others may be aggressive and require urgent medical attention. Liver tumors may develop as primary tumors originating in the liver or as secondary tumors that spread from other organs.
A specialist evaluation is essential to determine the type and severity of the tumor.