Ascites Treatment
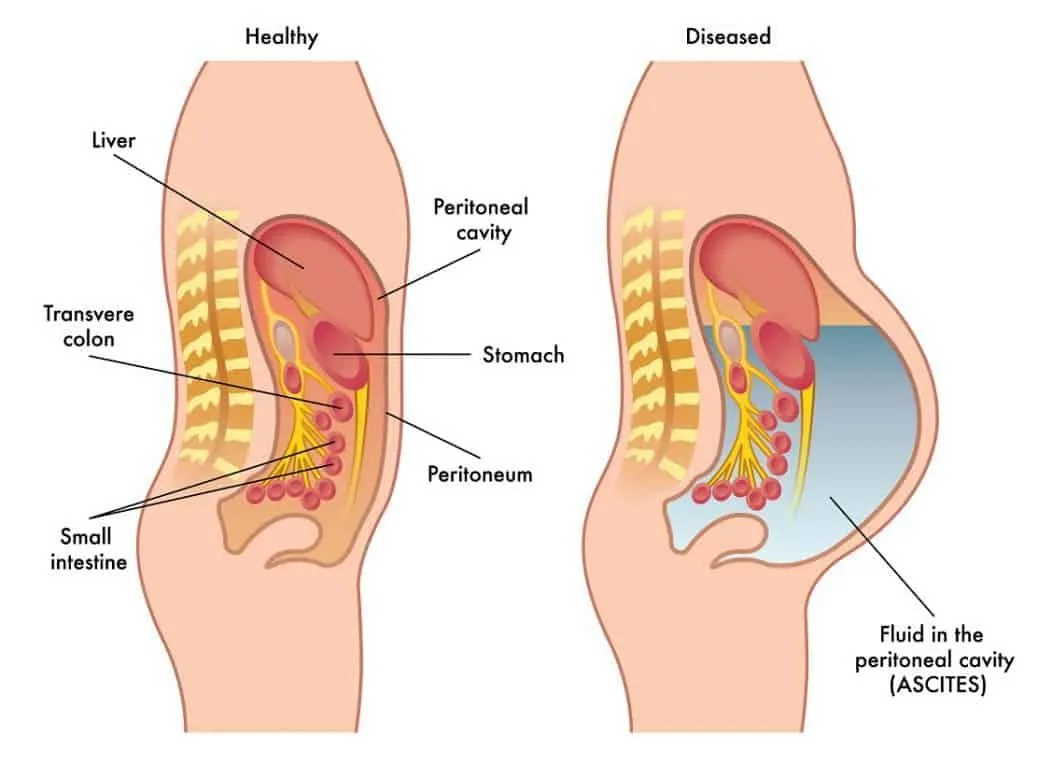
Ascites is a medical condition in which excess fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, leading to abdominal swelling and discomfort. It is most commonly associated with chronic liver disease but may also occur due to other medical conditions. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential to manage symptoms and prevent serious complications.
With timely medical care, accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment, ascites can be effectively controlled, improving comfort and overall quality of life.
What Is Ascites?
Ascites occurs when fluid builds up inside the abdomen, causing visible swelling and pressure. This fluid accumulation results from increased pressure in blood vessels or reduced protein levels in the blood, commonly due to liver dysfunction.
Ascites often develops gradually but can become severe if not treated promptly.